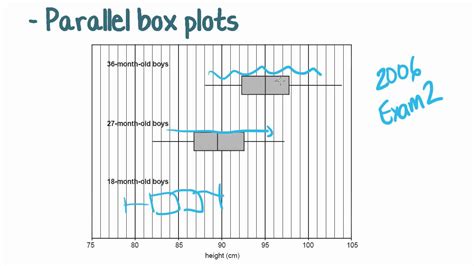
relationship between box plots and distribution graoh In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen. Side-by-side .
We provide superior sheet metal fabrication and assembly with cost-effective on-time manufacturing performance. United Fabrications has unparalleled experience in contract metal fabrication for a wide spectrum of industries.
0 · parallel box plots
1 · list of box plots
2 · how to draw a box plot
3 · how to create a box plot
4 · example of a box plot
5 · box plots in statistics
6 · box plots explained
7 · box plot calculation
Unique Metal Fabrication Incorporated 2888 N. Rotary Terrace PO Box 201 Pittsburg, KS 66762 620-232-3060
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum . Box plots are useful because they allow us to gain a quick understanding of the distribution of values in a dataset. They’re also useful for comparing two different datasets. When comparing two or more box plots, we . In this section, we present another important graph called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in-class experiment. Some graph types, such as stem-and-leaf displays, are best-suited for small to moderate amounts of data, whereas others, such as histograms, are best-suited for large .
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with .In statistics, a box plot is used to provide a visual summary of data. The distribution of data is shown through the positions of the median and the quartiles. From this, the spread and skew of the data can also be seen. Side-by-side . A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], .Graph types such as box plots are good at depicting differences between distributions. Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two variables. Histograms
Box Plots. How to Interpret a Box Plot in Terms of a Normal Distribution. One way to understand a box plot is to think of what a box plot of data from a normal distribution will look like. My aim is to create a plot/ graph to visualize the relationship between the binary variable TARGET_happiness (meaning "is the person happy?") and the categorical variable car (meaning "which car does this .
parallel box plots
The box in the box-plot represents 50% of the data, The green line in the middle of the box represents the median value of the data. The tails on each side of the box represent 25% data each. Understanding the distribution of a continuous . Relationships between things; Different Types of Graphs for Data Visualization. Data can be a jumble of numbers and facts. Charts and graphs turn that jumble into pictures that make sense. 10 prime super useful chart types . Graph types such as box plots are good at depicting differences between distributions. Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two variables. . {17}\) provides a revealing summary of the data. Since half the scores in a distribution are between the hinges (recall that the hinges are the 25th and 75th percentiles), we see that . Boxplot. A boxplot is sometimes known as the box and whisker plot.It shows the distribution of the quantitative data that represents the comparisons between variables. boxplot shows the quartiles of the dataset while the whiskers extend to show the rest of the distribution i.e. the dots indicating the presence of outliers. Syntax:
What is an appropriate graph to illustrate the relationship between two ordinal variables? A few options I can think of: Scatter plot with added random jitter to stop points hiding each other. . a box plot grouped by the levels of the independent variable. . but the shape of the distribution would be hard to discern at low-frequency levels .Every type of graph is a visual representation of data on diagram plots (ex. bar, pie, line chart) that show different types of graph trends and relationships between variables. Although it is hard to tell what are all the types of graphs, this page consists all of the common types of statistical graphs and charts (and their meanings) widely .
Shows possible relationships between multiple variables, looking at all two-way combinations. Additional graphs can be added: histograms for each variable to identify outliers, density ellipses for each scatter plot to identify multidimensional outliers, heatmaps of correlations to clarify possible relationships.Box Plots. We have already discussed techniques for visually representing data (see histograms and frequency polygons). In this section, we present another important graph, called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers (extreme scores) and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in .For example a pie chart or bar graph might be used to display the distribution of a categorical variable while a boxplot or histogram might be used to picture the distribution of a measurement variable. To study the relationship between two variables, a comparative bar graph will show associations between categorical variables while a .
A scatter plot is a type of data visualization that shows the relationship between different variables. This data is shown by placing various data points between an x- and y-axis.The stacked histogram emphasizes the part-whole relationship between the variables, but it can obscure other features (for example, it is difficult to determine the mode of the Adelie distribution. Another option is “dodge” the bars, which moves them horizontally and reduces their width.Chapter 6 Multivariate Graphs. In the last two chapters, you looked at ways to display the distribution of a single variable, or the relationship between two variables. We are usually interested in understanding the relations among several variables. Multivariate graphs display the relationships among three or more variables.
I would add the geom_boxplot() layer to create a box plot. Box plots present data in what is known as the five-number summary. The five numbers refer to percentiles of the data I’m working with. The five percentiles summarized by a box plot are the following: The largest value: Represented by the top of the black line extending from the top . These visualizations are used to describe the distribution and relationships between variables in your dataset. Boxplot. A boxplot summarizes the distribution of a single continuous variable by showing the medians and quartiles. The box at the center contains the middle 50 percent of the data. . you can create a side by side bar graph. For .
list of box plots
Bivariate graphs display the relationship between two variables. The type of graph will depend on the measurement level of each variable (categorical or quantitative). . A violin plots capture more a a distribution’s shape than a .
Box-and-whisker plots, also known as box plots, provide a concise summary of a dataset's distribution, displaying key statistics like median, quartiles, and outliers. Scatter plots, on the other hand, illustrate the relationship between two .
A box plot (also called a box and whisker plot) is a graph that presents information from a five-number summary. It does not show a distribution in as much detail as a stem and leaf plot or histogram does, but is especially useful for indicating whether a distribution is skewed and whether there are potential unusual observations (outliers) in the data set.$\begingroup$ For the discrete-discrete case, this answer to a somewhat related question here, on plotting ordered categorical data may help (though possibly without the boxes in your case).I'm really not sure how you think this 'bias' arises; it would affect the visual impression of the data points (leading to use expecting the line to go somewhere other than where it should) but not . How to interpret a box plot? A box plot gives us a basic idea of the distribution of the data. IF the box plot is relatively short, then the data is more compact. If the box plot is relatively tall, then the data is spread out. The interpretation of the compactness or spread of the data also applies to each of the 4 sections of the box plot.Visualizing categorical data#. In the relational plot tutorial we saw how to use different visual representations to show the relationship between multiple variables in a dataset. In the examples, we focused on cases where the main relationship was between two numerical variables. If one of the main variables is “categorical” (divided into discrete groups) it may be helpful to use a more .
A block plot is similar to a box plot, showing the importance of a particular factor in the data. [As shown in Fig 1] Just like ANOVA, it is used to show statistical significance. A block plot, also known as a block diagram or block chart, is a graphical representation of the relationship between different variables in a dataset. It is often used t
How to Graph a Boxplot. We use a boxplot below to analyze the relationship between a categorical feature (malignant or benign tumor) and a continuous feature (area_mean). There are a couple ways to graph a boxplot through Python. You can graph a boxplot through Seaborn, Matplotlib or pandas. Graphing a Boxplot With SeabornVisualizing categorical data#. In the relational plot tutorial we saw how to use different visual representations to show the relationship between multiple variables in a dataset. In the examples, we focused on cases where the main relationship was between two numerical variables. If one of the main variables is “categorical” (divided into discrete groups) it may be helpful to use a more . The example below creates three boxplots in one chart, each summarizing a data sample drawn from a slightly different Gaussian distribution. Each data sample is created as an array and all three data sample arrays are added to a list that is padded to the plotting function.
Scatter plots are used to display the relationship between two continuous variables x and y. In this article, we’ll start by showing how to create beautiful scatter plots in R. We’ll use helper functions in the ggpubr R package to display automatically the correlation coefficient and the significance level on the plot.. We’ll also describe how to color points by groups and to add .Scatter plot is a graph in which the values of two variables are plotted along two axes. It is a most basic type of plot that helps you visualize the relationship between two variables. Concept What is a Scatter plot? Basic Scatter plot in python Correlation with Scatter plot Changing the color of groups of . Python Scatter Plot – How to visualize relationship between two numeric features .
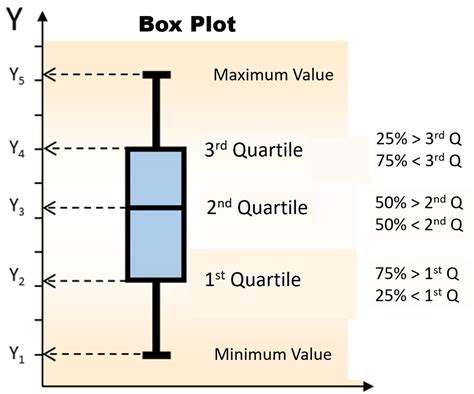
how to draw a box plot
how to create a box plot
Light Duty Underground Box, Material: Reinforced Concrete, W x L x D: 16" x 25" x 12", Color: Gray. **Lids Sold Separately**
relationship between box plots and distribution graoh|parallel box plots