box plot distribution skew In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to . VINTAGE 1980 STRAWBERRY SHORTCAKE Metal Lunch Box & Plastic Thermos.
0 · understanding box plots for dummies
1 · positively skewed box plots
2 · positive skew vs negative boxplot
3 · left vs right skewed boxplot
4 · examples of skewed box plots
5 · boxplots for dummies
6 · box plot for right skewed
7 · box and whisker diagram skewness
$9.99
In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum .
To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and .In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to .
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, .
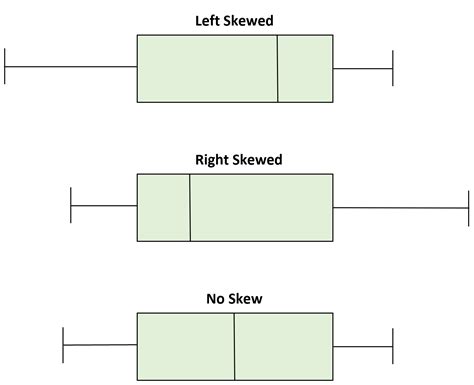
In a distribution with positive skewness (right-skewed): The right tail of the distribution is longer or fatter than the left. The mean is greater than the median, and the mode is less than both mean and median.
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or symmetrical, provides crucial insights into data characteristics. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to analyze them. Let’s start by contrasting characteristics of the symmetrical normal distribution with skewed distributions.
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
In a distribution with positive skewness (right-skewed): The right tail of the distribution is longer or fatter than the left. The mean is greater than the median, and the mode is less than both mean and median. We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right . In this journey through “Box Plot Skewness: Decoding Asymmetry,” we’ve unlocked the secrets of box plots and their role in revealing data distribution. We’ve seen how skewness, whether right, left, or symmetrical, provides crucial insights into data characteristics.
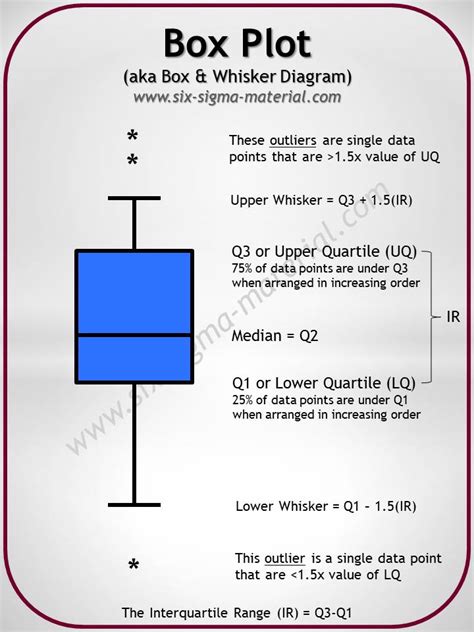
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.To determine whether a distribution is skewed in a box plot, look at where the median line falls within the box and whiskers. You have a symmetrical distribution when the box centers approximately on the median line, and the upper and lower whiskers are about equal length.In this post, learn about left and right skewed distributions, how to tell the differences in histograms and boxplots, the implications of these distributions, why they occur, and how to analyze them. Let’s start by contrasting characteristics of the symmetrical normal distribution with skewed distributions.
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left, or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
understanding box plots for dummies
positively skewed box plots
Create a box plot for the data from each variable and decide, based on that box plot, whether the distribution of values is normal, skewed to the left or skewed to the right, and estimate the value of the mean in relation to the median.
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .
positive skew vs negative boxplot
left vs right skewed boxplot
examples of skewed box plots

Top 10 Best Iron Work in Vista, CA - October 2024 - Yelp - Elar Welding, Carney Fence, McMaster Iron, Abel & Brothers Custom Iron Works, MJ Wrought Iron, Fence Plus, North County Iron Works, Martinez Welding, American Fence Concepts, Banister Iron Works
box plot distribution skew|left vs right skewed boxplot